How to Do Try Again in C#
C for Loop
In this tutorial, you volition learn to create for loop in C programming with the assistance of examples.
Video: C while Loop
In programming, a loop is used to repeat a block of code until the specified condition is met.
C programming has 3 types of loops:
- for loop
- while loop
- do...while loop
We will acquire about for loop in this tutorial. In the next tutorial, we volition acquire nearly while and do...while loop.
for Loop
The syntax of the for loop is:
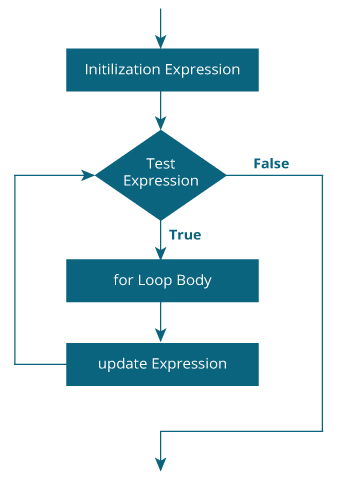
for (initializationStatement; testExpression; updateStatement) { // statements within the body of loop } How for loop works?
- The initialization argument is executed merely in one case.
- And then, the test expression is evaluated. If the test expression is evaluated to false, the
forloop is terminated. - Notwithstanding, if the exam expression is evaluated to true, statements inside the body of the
forloop are executed, and the update expression is updated. - Again the test expression is evaluated.
This process goes on until the test expression is imitation. When the examination expression is false, the loop terminates.
To learn more about test expression (when the test expression is evaluated to true and false), cheque out relational and logical operators.
for loop Flowchart
Example 1: for loop
// Impress numbers from ane to ten #include <stdio.h> int main() { int i; for (i = 1; i < 11; ++i) { printf("%d ", i); } render 0; } Output
1 2 three 4 v 6 7 eight 9 x
- i is initialized to 1.
- The exam expression
i < elevenis evaluated. Since 1 less than 11 is true, the body offorloop is executed. This volition impress the 1 (value of i) on the screen. - The update statement
++iis executed. At present, the value of i will exist ii. Again, the test expression is evaluated to true, and the body offorloop is executed. This volition impress 2 (value of i) on the screen. - Again, the update argument
++iis executed and the test expressioni < 11is evaluated. This process goes on until i becomes 11. - When i becomes 11, i < 11 will be false, and the
forloop terminates.
Example 2: for loop
// Program to calculate the sum of first n natural numbers // Positive integers 1,two,3...n are known as natural numbers #include <stdio.h> int main() { int num, count, sum = 0; printf("Enter a positive integer: "); scanf("%d", &num); // for loop terminates when num is less than count for(count = 1; count <= num; ++count) { sum += count; } printf("Sum = %d", sum); return 0; } Output
Enter a positive integer: ten Sum = 55
The value entered by the user is stored in the variable num. Suppose, the user entered x.
The count is initialized to 1 and the examination expression is evaluated. Since the test expression count<=num (1 less than or equal to ten) is true, the body of for loop is executed and the value of sum will equal to 1.
So, the update argument ++count is executed and count will equal to two. Over again, the test expression is evaluated. Since two is as well less than 10, the exam expression is evaluated to true and the body of the for loop is executed. Now, sum volition equal iii.
This process goes on and the sum is calculated until the count reaches 11.
When the count is xi, the test expression is evaluated to 0 (false), and the loop terminates.
Then, the value of sum is printed on the screen.
We will learn about while loop and do...while loop in the next tutorial.
edmondstoneinvuld.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.programiz.com/c-programming/c-for-loop